|
Objectives of the Semantic Web
-
Today's Web is designed for presentation of content to humans.
-
Humans are expected to interpret and understand the meaning of the content.
The Semantic Web is an extension of the current web. It aims to:
-
Give information a well-defined meaning, thereby
creating a pathway for machine-to-machine communication and
automated serives based on descriptions of semantics.
Modeling
The Semantic Web Layer Cake
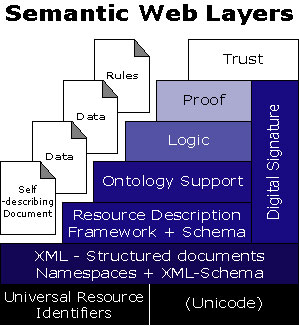
Figure 1. The Semantic Web Layer Cake (Berners-Lee, 2002).
|
The Semantic Web is an extension of the current web.
-
URIs are just links in today's web.
Unicode is 16-bit representation of (multilingual) characters.
-
XML files and web resources capture objects and classes.
XML separates structure from presentation.
XML assumes data/information can be represented in hierarchies.
-
RDF (resource description framework) describes relationships
between objects and classes in a general but simple way.
RDF separates content from structure, thereby allowing for the
merging of multiple conceptual models.
RDF represents data/information in graphs.
-
Ontologies provide a formal conceptualization (semantic representation)
of a particular domain shared by a group of people.
Languages include: Darpa Agent Markup Language (DAML) and Web Ontology Language (OWL).
-
The logic layer allows for reasoning.
Languages include: RuleML.
Reasoning tools include Jess and MANDARAX.
-
Ontology-based applications will be built on top
of the Semantic Web infrastructure (i.e., XML, RDF and ontologies)
|
|
![[Left]](images/button-left.gif)
![[Up]](images/button-up.gif)
![[Right]](images/button-right.gif)
![[Left]](images/button-left.gif)
![[Up]](images/button-up.gif)
![[Right]](images/button-right.gif)
![[Left]](images/button-left.gif)
![[Up]](images/button-up.gif)
![[Right]](images/button-right.gif)
![[Left]](images/button-left.gif)
![[Up]](images/button-up.gif)
![[Right]](images/button-right.gif)
![[Left]](images/button-left.gif)
![[Up]](images/button-up.gif)
![[Right]](images/button-right.gif)